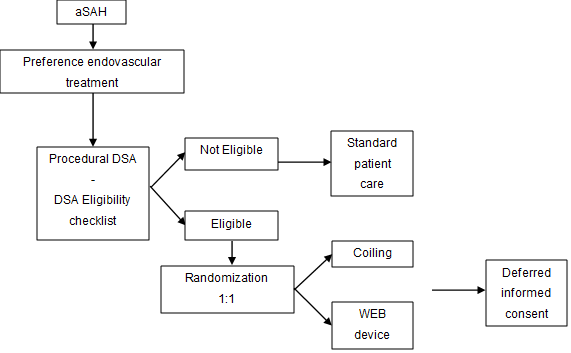
Study design
Design
We will perform a prospective randomized controlled pilot trial in aSAH patients in the Netherlands and Belgium. The study is set up as a randomized two-arm trial and patients will be randomized 1:1 into two groups (coiling versus WEB).
Population
Aneurysmal SAH patients WFNS grade I-IV, aged ≥18 will be eligible for inclusion if the ruptured aneurysm is eligible for both intrasaccular (WEB) treatment and standard coiling. Typically, patients with a small-neck aneurysm will be included.
In- and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria
In order to be eligible to participate in this trial, the subject must meet all the following criteria:
Patient admitted with aneurysmal SAH, confirmed by plain head CT and CTA
Age older than 18 years
Ruptured aneurysm eligible for both intrasaccular (WEB) treatment and standard coiling (based on the local practitioner’s opinion)
WFNS grade I-IV
Indication for endovascular treatment according to local practice and expertise.
Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria are:
Post procedure patient (or representative) unable or unwilling to provide informed consent
WFNS grade V
Patient with a non-saccular aneurysm
Patient with an aneurysm with width less than 2mm or more than 10mm
Patient with an aneurysm with height less than 2,5mm
Main study parameters
Primary endpoints:
- Primary feasibility outcome
- Consent rate
- We will track how many randomized patients later agree to participate through deferred consent.
- Cross-over rate (exploratory outcome)
- Inclusion progress (exploratory outcome)
- Eligibility Rate (exploratory outcome)
- Through this fully anonymous checklist, we can also assess the reasons for not including patients in the study.
- Consent rate
- The secondary outcomes will be used to power a subsequent phase 3 trial (aneurysm occlusion as primary clinical outcome).
Secondary endpoints:
- Aneurysm occlusion (modified Raymond Roy classification (mRR) for coiling and the WEB occlusion scale (WOS) for WEB)
- Procedure time (minutes)
- Fluoroscopy time (minutes)
- Radiation dose (Cumulative dose (CD) / Dose area product (DAP) (in Gy))
- Antithrombotic medication use, during and post procedural
- Complications related to treatment of the ruptured aneurysm(13-16)
- Complications related to SAH
- mRS after 6 months ± 30 days after aSAH systematically evaluated by an independent study nurse or coordinator.
- Treatment costs
Randomization
The study is set up as an open randomized two-arm trial and patients will be randomized 1:1 into two groups (coiling versus WEB). Randomization is done via a web based random generator (CASTOR). This study has a PROBE design (open-label study with blinded endpoint assessment). Block randomization will be used to ensure equal distribution in both groups.
Sample size
We anticipate an inclusion of 60 patients across 7 different centres for the pilot study, 30 patients in the intra saccular device group and 30 patients in the standard coiling group. With an estimated mortality of around 20% in the WFNS 1-4 patients and possible withdrawals, we aim to have 20 patients available for 6 months follow-up per group.
Informed consent
Patients will be enrolled using a deferred consent procedure in accordance with the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act (WMO)(19). Written informed consent to continue participation in the study will be obtained from the patient or their representative by trained research personnel, 72 hours after procedure.
The rationale for the deferred consent is that patients with aSAH should undergo repair of their aneurysm as soon as it is feasible, preferably within 24 hours, to reduce the risk of aneurysm rerupture which is frequently fatal (at latest within 72 hours).
Patients admitted in one of the tertiary SAH referral centers in the Netherlands or Belgium with a ruptured aneurysm during day time, are often treated within several hours.
The choice of treatment modality of the ruptured aneurysm, surgical or endovascular, is based on local standards. If there is an intention for endovascular treatment, the patient is anesthetized for the endovascular procedure. At the start of the endovascular procedure, diagnostic angiography is always performed. Based on this DSA, more precise the 3D angiography, the performing physician can assess whether the aneurysm is suitable for both coiling and WEB. If the aneurysm to be treated is suitable for both standard coiling and WEB device, randomization will be performed via the online randomizer.
Since this is an emergency procedure and potential inclusion as well as randomization can only take place at the time of treatment, when the patient is under anesthesia, deferred consent is applied.
Flow chart inclusion and consent